Medical management of congestive heart failure pdf
Medical management of congestive heart failure pdf
In Surgical Management of Congestive Heart Failure, James C. Fang, MD, and Gregory S. Couper, MD, have assembled a panel of prominent surgeons and cardiologists to review the latest clinical, scientific, and investigational surgical and mechanical approaches to heart failure in hopes of improving the lives of this challenging group of patients. Topics range from such traditional strategies as
Congestive Heart Failure: Understanding the Pathophysiology and Management Lynn Fletcher, MSN, ARNP Debera Thomas, DNS, ARNP Purpose To explain key concepts involved in the devel- opment and management of congestive heart failure (CHF). An overview of medications commonly used in the treatment of CHF is also presented. Data Sources Selected clinical articles, major research stud- ies, …
Society Guidelines Presentation, Diagnosis, and Medical Management of Heart FailureinChildren:CanadianCardiovascularSocietyGuidelines Paul F. Kantor, MBBCh,a,b Jane
Congestive Heart Failure, multiple different procedures for heart failure are presented, together with careful description of the candidate popu- lations for each.
Congestive Heart Failure Management Plan 1. Green means Go. Follow medication, weight, and diet advice.
Congestive heart failure (CHF) complicates the course of a significant proportion of patients in the intensive care unit (ICU). In the ICU, CHF may present as a manifestation of newly diagnosed cardiac disease or as an exacerbation of underlying heart disease, as a result of fluid overload or stress
Featuring contributions from leaders in the fields of heart failure, cardiac transplantation, cardiac pathology, and cardiovascular molecular research, Congestive Heart Failure and Cardiac Transplantation is a valuable compendium for cardiologists, cardiothoracic surgeons, researchers, trainees, and students.
Congestive heart failure is a clinical syndrome characterized by (1) signs or symptoms of volume overload or (2) manifestations of impaired tissue perfusion such as …
The role of angiotensin receptor antagonists in treating congestive heart failure is discussed. Medical Pharmacology Chapter 10: Management of Congestive Heart Failure Pharmacological and Physiological Principles . Heart Failure: Pharmacological Treatment . Angiotensin Receptor Antagonists (Blockers): 336. Inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system may also be accomplished by …
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a common clinical problem and in its advanced stage has a poor prognosis. Approximately 400 000 individuals develop heart failure each year (Parmley 1989).
The evolution of prehospital treatment of decompensated congestive heart failure has in some ways come full circle: rather than emphasizing a battery of new pharmacotherapies, out-of-hospital providers have a renewed focus on aggressive use of nitrates, optimization of airway support, and rapid transport.
Medical management of congestive heart failure.

Congestive Heart Failure Wiley Online Library
Medical Management of Congestive Heart FailureDrugs Used in Management of Congestive Heart Failure y y y Dig… Scribd is the world’s largest social reading and publishing site. Search Search
Management of Congestive Heart Failure Definition : Heart failure is a common clinical syndrome characterized by dyspnea, fatigue, and signs of volume overload, which may include peripheral edema and pulmonary rales.
Congestive Heart Failure: Understanding the Pathophysiology and Management Lynn Fletcher, MSN, ARNP Debera Thomas, DNS, ARNP Purpose To explain key concepts involved in the devel- opment and management of congestive heart failure (CHF). An overview of medications commonly used in the treatment of CHF is also presented. Data Sources Selected clinical articles, major …
PDF Audience: This article is designed for primary care physicians, cardiovascular specialists, medical directors, and other managed care administrators responsible for heart failure patients.
Congestive heart failure causes substantial patient morbidity and mortality in the United States. Symptoms and physical findings can be helpful in diagnosis but have limited sensitivity and specificity. Objective measurement of ventricular function is essential in virtually all patients in whom a diagnosis of heart failure is suspected.
The management of congestive heart failure. Left ventricular dysfunction develops through ventricular remodeling. This leads to arrhythmia, pump failure, and death.
been hospitalized for heart failure, disease management programs and telemonitoring can reduce hospitalizations and mortality. ( Am Fam Physician . 2017;95(1):13-20.
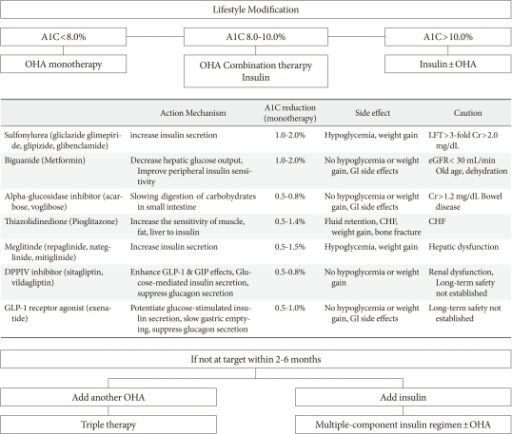
Despite modern management, congestive heart failure proved to be extremely lethal. The probability of dying within five years from onset of congestive heart failure was 62 per cent for men and 42
Management of Congestive Heart Failure BACKGROUND Heart failure (HF) is a major and growing public health problem in the United States. Approximately 5 million patients in the country have heart failure and there will be approximately 550,000 new cases of heart failure each year. Heart failure accounts for approximately 12 to 15 million office visits each year and 6.5 million hospital days
7/08/2001 · Dr. Giannetti is Medical Director of the Heart Failure and Heart Transplant Centre, McGill University Health Centre, Montreal, Que. Next Section We are making great progress in controlling the epidemic of coronary artery disease that plagued much of the last century.
Prehospital Management of Congestive Hear t Failure Amal Mattu, MD, FACEP, FAAEM*, Benjamin Lawner, DO, EMT-P KEYWORDS Congestive heart failure Pulmonary edema Prehospital Noninvasive ventilation The prehospital evaluation and treatment of standard is not uniformly followed.1 State EMS decompensated congestive heart

TITLE: Management of Congestive Heart Failure in Primary and Community Care: Guidelines. DATE: 23 July 2013 . RESEARCH QUESTION . What are the evidence-based guidelines regarding the management of congestive heart failure in primary care or community-based settings? KEY MESSAGE . Eight evidence-based guidelines were identified regarding the management of congestive heart failure …
Management of chronic heart failure Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (also referred to as HF with systolic dysfunction) is defined as the presence of signs and symptoms of HF with a left ventricular ejection fraction of <40% (although the
The main goal of the treatment of acute congestive heart failure (CHF) is to provide symptomatic relief. Initial management options include a combination of oxygen, diuretics, ultra-filtration, vasodilators, inotropes, and vasopressors.
Presentation Diagnosis and Medical Management of Heart
1 CardioMEMS™ HF System (St. Jude Medical) and Sacubitril/Valsartan (Entresto™, Novartis) for Management of Congestive Heart Failure:
Preface. Special Topic Issue: Cardiology 2004, Vol. 101, No. 1-3 Congestive heart failure (CHF) is one of the most common killers worldwide and is becoming more prevalent as the population continues to …
The role of digitalis glycosides iin managing congestive heart failure is described. Medical Pharmacology Chapter 10: Management of Congestive Heart Failure Pharmacological and Physiological Principles . Heart Failure: Pharmacological Treatment . Digitalis Glycosides: Digitalis glycosides historically were the central pharmacological therapy for congestive heart failure. 3 36. …
Special Topic Issue: Cardiology 2004, Vol. 101, No. 1-3 Congestive heart failure (CHF) is one of the most common killers worldwide and is becoming more prevalent as the population continues to age. Despite great advances in medical drug treatment and the liberal use of pacemakers and internal – medical lab technician resume pdf Management of Congestive Heart Failure OBJECTIVE The objective of this Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) is to provide evidence-based practice recommendations for the treatment of Congestive Heart Failure (CHF). The CPG discusses care management issues such as goals to support the Member in attaining treatment goals and lifestyle modifications. Behavioral health implications and Measureable
The medical management of patients with chronic congestive heart failure (CHF) has evolved considerably over the last two decades. In addition to the availability of new agents with proven clinical efficacy, we now know a great deal more about where and when to use (or sometimes avoid) traditional
Congestive heart failure is a common condition that increases in prevalence with increasing age. In 2003, guidance from the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence acknowledged that the “rising epidemic of heart failure” is partly the result of people living longer and the more effective treatments for coronary heart disease
The four chronic conditions include congestive heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes mellitus, conditions or medications causing xerostomia. I. Congestive heart failure (CHF) represents a symptom complex that can be caused by a number of specific disease processes.
Congestive heart failure is a chronic, debilitating illness, with increasing prevalence in the elderly. It is one of the most common causes for hospital admission, and associated treatment costs are es-timated at .2 billion. Despite improved survival with medical therapy, beneficial effects on quality of life have not been consistently reported. In ad-dition, optimum medical therapy, as
This is an important factor contributing to the increased incidence of congestive heart failure (CHF), the cardiovascular condition most rapidly on the rise. CHF currently affects an estimated 200 000 to 300 000 Canadians. 1 The morbidity and mortality associated with this condition are substantial.
Management of Congestive Heart Failure CARE MANAGEMENT OVERVIEW Heart failure (HF) is a major and growing public health problem in the United States. Approximately 5 million Americans have heart failure and there will be approximately 550,000 new cases of heart failure each year. Heart failure accounts for approximately 12 to 15 million office visits each year and 6.5 million hospital …
effective way to augment medical management of CHF. Given the incompleteness of CHF medical management and the exploding interest in comple-mentary medical intervention, it seems imperative that further work in psychosocial treatment be undertaken. (Prev Cardiol. 2002;5:168–172, 176) ©2002 CHF, Inc. Congestive heart failure (CHF) is the only major cardiovascular disorder that is increasing
of congestive heart failure. Study Selection Randomized controlled trials of therapy for 150 patients or more were included if advanced heart failure was represented.
Management of Congestive Heart Failure WellCare
Chronic heart failure may be compensated and stable with few signs and baseline symptoms, or decompensated with a recent clinical deterioration and physical evidence of …
Management of Congestive Heart Failure Definition: Heart failure is a common clinical syndrome characterized by dyspnea, fatigue, and signs of volume overload, which may include peripheral edema and pulmonary rales. There is no single diagnostic test for heart failure; therefore, it remains a clinical diagnosis requiring a history, physical examination, diagnostic and laboratory testing
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is the most common cause of premature death before the age of 75 years in the UK. It is also the most common cause of heart failure in western countries, responsible for an estimated 70% of heart failure cases in the UK.
Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (EF ≥ 40%) For patients with HF-pEF the goals of pharmacologic management are to optimize risk factors for disease progression/ decompensation, and control signs/symptoms of HF (e.g., heart rate, blood pressure, volume status).
Prehospital Management of Congestive Heart Failure AmalMattu,MD,FACEP,FAAEM *,BenjaminLawner,DO,EMT-P The prehospital evaluation and treatment of decompensated congestive heart failure (CHF) is
Medical Bulletin VOL.11 NO.7 JULY 2006 22 Treatment of Congestive Cardiac Failure Congestive cardiac failure, whether due to systolic or diastolic heart failure, is a common cause for hospital
Medical management of congestive heart failure. A. E. Arai and B. H. Greenberg The syndrome of congestive heart failure can result from a variety of cardiac disorders of which left ventricular dysfunction is the most common. The clinical presentation is determined by the interaction between cardiac dysfunction and a series of compensatory mechanisms that are activated throughout the …
Surgical Options for the Management of Congestive Heart Failure PDF Free Download, Surgical Options for the Management of Congestive Heart Failure PDF ,
Prehospital Management of Congestive Heart Failure

The Medical Management of Chronic Congestive Heart Failure
Download Surgical Management of Congestive Heart Failure PDF. James C. Fang, MD, and Gregory S. Couper, MD, have assembled a panel of prominent surgeons and cardiologists to review the latest clinical, scientific, and investigational surgical and mechanical approaches to heart failure in hopes of improving the lives of this challenging group of
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is the leading cause of hospitalization in individuals 65 years of age and older. The difficulty in diagnosing CHF is that symptoms are not specific and are observed in many disease processes.
Management of Congestive Heart Failure Chicago

Download Surgical Management of Congestive Heart Failure
Medical pharmacology Drug Management of Congestive Heart


CardioMEMS™ HF (St. Jude Medical) (Entresto™ Novartis
Treatment of Congestive Cardiac Failure fmshk.org
medical marijuana delivery service handbook pdf – Treatment of Congestive Heart Failure Guidelines for the
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE

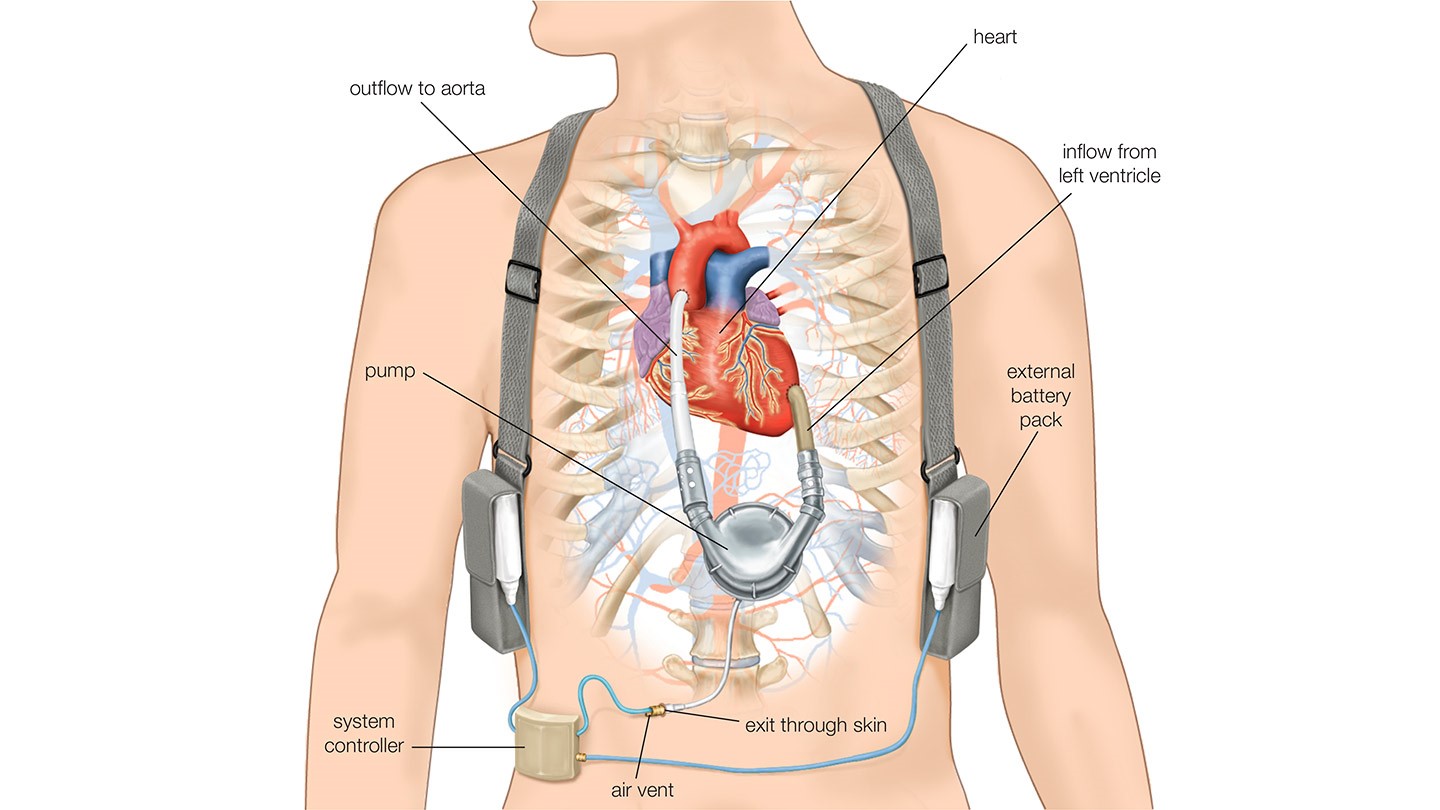
Medical Management of Advanced Heart Failure
Medical Pharmacology Pharmacological Management of
Management of Congestive Heart Failure Chicago Medicaid
Congestive Heart Failure Wiley Online Library
been hospitalized for heart failure, disease management programs and telemonitoring can reduce hospitalizations and mortality. ( Am Fam Physician . 2017;95(1):13-20.
of congestive heart failure. Study Selection Randomized controlled trials of therapy for 150 patients or more were included if advanced heart failure was represented.
The evolution of prehospital treatment of decompensated congestive heart failure has in some ways come full circle: rather than emphasizing a battery of new pharmacotherapies, out-of-hospital providers have a renewed focus on aggressive use of nitrates, optimization of airway support, and rapid transport.
Congestive heart failure is a common condition that increases in prevalence with increasing age. In 2003, guidance from the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence acknowledged that the “rising epidemic of heart failure” is partly the result of people living longer and the more effective treatments for coronary heart disease
Management of Congestive Heart Failure Definition : Heart failure is a common clinical syndrome characterized by dyspnea, fatigue, and signs of volume overload, which may include peripheral edema and pulmonary rales.
The main goal of the treatment of acute congestive heart failure (CHF) is to provide symptomatic relief. Initial management options include a combination of oxygen, diuretics, ultra-filtration, vasodilators, inotropes, and vasopressors.
7/08/2001 · Dr. Giannetti is Medical Director of the Heart Failure and Heart Transplant Centre, McGill University Health Centre, Montreal, Que. Next Section We are making great progress in controlling the epidemic of coronary artery disease that plagued much of the last century.
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is the most common cause of premature death before the age of 75 years in the UK. It is also the most common cause of heart failure in western countries, responsible for an estimated 70% of heart failure cases in the UK.
Featuring contributions from leaders in the fields of heart failure, cardiac transplantation, cardiac pathology, and cardiovascular molecular research, Congestive Heart Failure and Cardiac Transplantation is a valuable compendium for cardiologists, cardiothoracic surgeons, researchers, trainees, and students.
Management of Congestive Heart Failure Definition: Heart failure is a common clinical syndrome characterized by dyspnea, fatigue, and signs of volume overload, which may include peripheral edema and pulmonary rales. There is no single diagnostic test for heart failure; therefore, it remains a clinical diagnosis requiring a history, physical examination, diagnostic and laboratory testing
The medical management of patients with chronic congestive heart failure (CHF) has evolved considerably over the last two decades. In addition to the availability of new agents with proven clinical efficacy, we now know a great deal more about where and when to use (or sometimes avoid) traditional
The evolution of prehospital treatment of decompensated congestive heart failure has in some ways come full circle: rather than emphasizing a battery of new pharmacotherapies, out-of-hospital providers have a renewed focus on aggressive use of nitrates, optimization of airway support, and rapid transport.
Management of congestive heart failure. Postgraduate
Management of Congestive Heart Failure OBJECTIVE The objective of this Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) is to provide evidence-based practice recommendations for the treatment of Congestive Heart Failure (CHF). The CPG discusses care management issues such as goals to support the Member in attaining treatment goals and lifestyle modifications. Behavioral health implications and Measureable
The Medical Management of Chronic Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a common clinical problem and in its advanced stage has a poor prognosis. Approximately 400 000 individuals develop heart failure each year (Parmley 1989).
Medical management of congestive heart failure.
Featuring contributions from leaders in the fields of heart failure, cardiac transplantation, cardiac pathology, and cardiovascular molecular research, Congestive Heart Failure and Cardiac Transplantation is a valuable compendium for cardiologists, cardiothoracic surgeons, researchers, trainees, and students.
Medical management of congestive heart failure.
Presentation Diagnosis and Medical Management of Heart
The medical management of patients with chronic congestive heart failure (CHF) has evolved considerably over the last two decades. In addition to the availability of new agents with proven clinical efficacy, we now know a great deal more about where and when to use (or sometimes avoid) traditional
Medical pharmacology Drug Management of Congestive Heart